In recent years, integrating traditional healing practices into modern healthcare has gained significant attention, with acupuncture emerging as a prominent player. In particular, acupuncture’s potential to address complex dermatological conditions such as eczema has piqued the curiosity of both patients and medical professionals. This article explores the use of acupuncture for eczema treatment, highlighting this ancient practice’s holistic principles. It provides a comprehensive overview of how acupuncture’s holistic approach may offer a unique perspective in the management of eczema, paving the way for potentially more well-rounded and effective treatment strategies.
What is Acupuncture?
Acupuncture, a foundational component of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), is an intricate healing technique that involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points of the body. Each acupuncture point is believed to correspond to different organs, bodily functions, and emotional states, making the practice a physical intervention and a holistic approach that addresses the interconnectedness of mind, body, and spirit.
Acupuncture stimulates the body’s natural healing mechanisms, promoting blood circulation, alleviating pain, and restoring equilibrium to various physiological processes. While its precise mechanisms are still under investigation, acupuncture’s popularity has expanded beyond its traditional origins, finding its place as a complementary or alternative therapy in modern healthcare for many conditions, including pain management, stress reduction, and even skin disorders like eczema.
How is Acupuncture Used for Eczema?
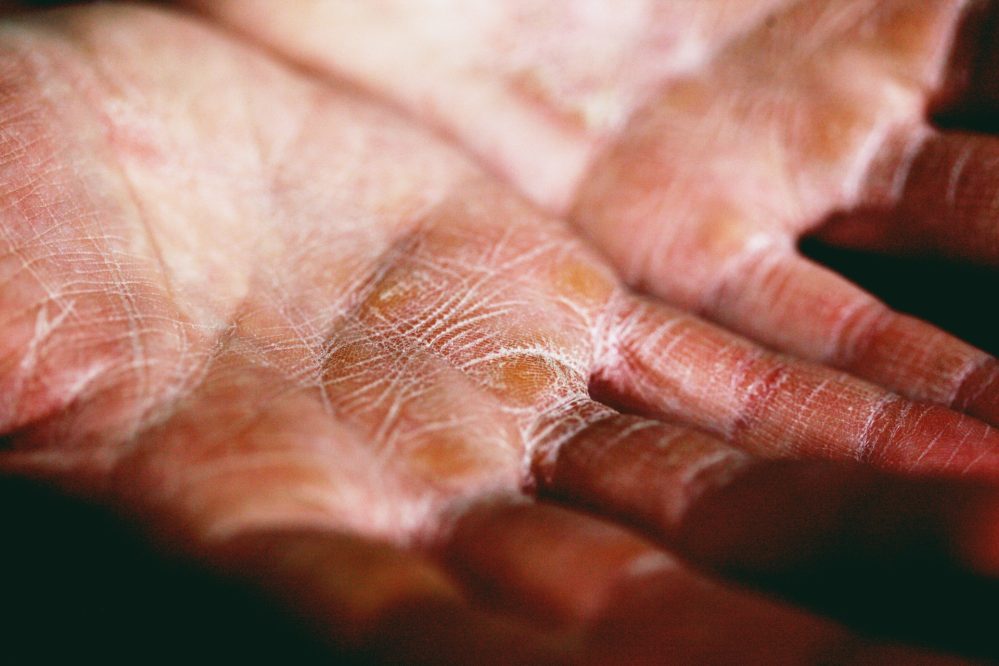
Eczema, a common and chronic skin condition, is characterized by inflammation, itchiness, and rash formation. It often presents a multifaceted challenge due to its complex interplay of genetic, environmental, and immunological factors. Acupuncture offers a distinctive approach to addressing eczema by harnessing the body’s ability to restore balance and harmony.
In this context, acupuncture’s application involves the insertion of fine needles into specific acupuncture points along the body’s meridians. By stimulating these points, acupuncture is believed to encourage the flow of energy (Qi) and blood, helping to regulate the immune response, reduce inflammation, and promote overall skin health. Moreover, acupuncture’s influence on the nervous system may contribute to the alleviation of itching sensations, a hallmark of eczema. Through its comprehensive approach that considers the condition’s physical and energetic aspects, acupuncture presents a potential avenue for managing eczema that extends beyond conventional treatments.
Acupuncture pressure points for eczema treatment
In acupuncture, specific pressure points are pivotal in addressing eczema by targeting the body’s energy pathways and promoting balance. While treatment strategies can be tailored to individual cases, several key acupuncture points have been identified for their potential efficacy in managing eczema symptoms.
One such point is LI11 (Quchi), located on the outer elbow crease. This point is associated with regulating immune responses and promoting skin health. Another significant point is SP10 (Xuehai), situated on the inner thigh, believed to aid in clearing body heat and dampness, which often contributes to eczema flare-ups. Additionally, the acupoint LV3 (Taichong) on the foot’s dorsum has been noted for its potential to alleviate skin disorders through its impact on liver function and blood circulation. Acupuncturists aim to harmonize the body’s energy flow by strategically selecting and stimulating these pressure points, potentially relieving and improving eczema symptoms.
The benefits of Acupuncture for Eczema
Using acupuncture points for eczema treatment provides a range of potential benefits that extend beyond conventional medical interventions. By targeting the condition’s physical and energetic aspects, acupuncture seeks to address the underlying imbalances that contribute to eczema development and exacerbation. One notable advantage is its ability to alleviate itching, a predominant and distressing symptom of eczema, through its influence on the nervous system. Acupuncture’s capacity to stimulate blood circulation and regulate immune responses may contribute to reducing inflammation, redness, and swelling commonly associated with eczema flare-ups.
Furthermore, this ancient practice encourages relaxation and stress reduction, which can be particularly beneficial as stress exacerbates eczema symptoms. As acupuncture seeks to restore overall balance within the body, its potential to improve sleep patterns and enhance the body’s natural healing mechanisms further solidifies its role as a holistic approach to eczema management.
Who Should Avoid Acupuncture?
While acupuncture is generally considered safe and well-tolerated, there are certain circumstances and individuals for whom caution or avoidance is recommended:
— Individuals with bleeding disorders or those taking anticoagulant medications.
— Pregnant women, especially during the first trimester, unless under the guidance of a qualified practitioner.
— People with a history of seizures or epilepsy.
— Those with a fear of needles or needle-related phobias.
— Individuals with compromised immune systems.
— Patients with skin infections or open wounds at the acupuncture points.
Possible Risks of Acupuncture
Although acupuncture is relatively safe when performed by trained and licensed practitioners, there are potential risks associated with the practice. These risks include:
— Infection: If proper sterilization protocols are not followed, there is a risk of infection at the insertion site.
— Bruising and Bleeding: Some mild bruising or bleeding may occur at the needle insertion points, particularly for individuals with bleeding disorders.
— Pain or Discomfort: While acupuncture is often well-tolerated, some individuals might experience temporary pain, discomfort, or tingling sensations during or after treatment.
— Organ Injury: In rare cases, there is a risk of injury to underlying organs, especially if needles are improperly placed or manipulated.
— Needle Sensitivity: Individuals may have varying levels of sensitivity to needle insertion, and some could experience adverse reactions.
It’s important for individuals considering acupuncture to consult with a qualified healthcare provider, disclose their medical history, and ensure they are receiving treatment from a licensed and reputable acupuncturist to minimize potential risks and ensure a safe experience.
Wrapping up
In eczema treatment, the holistic approach of acupuncture opens new avenues for exploration. By blending traditional principles with modern understanding, this practice offers a promising perspective for addressing the challenges of eczema. As we continue to bridge the gap between ancient wisdom and current knowledge, acupuncture’s role in enhancing our approach to eczema underscores the value of holistic and personalized therapies in modern healthcare.